Protozoans are unicellular, microscopic in size and d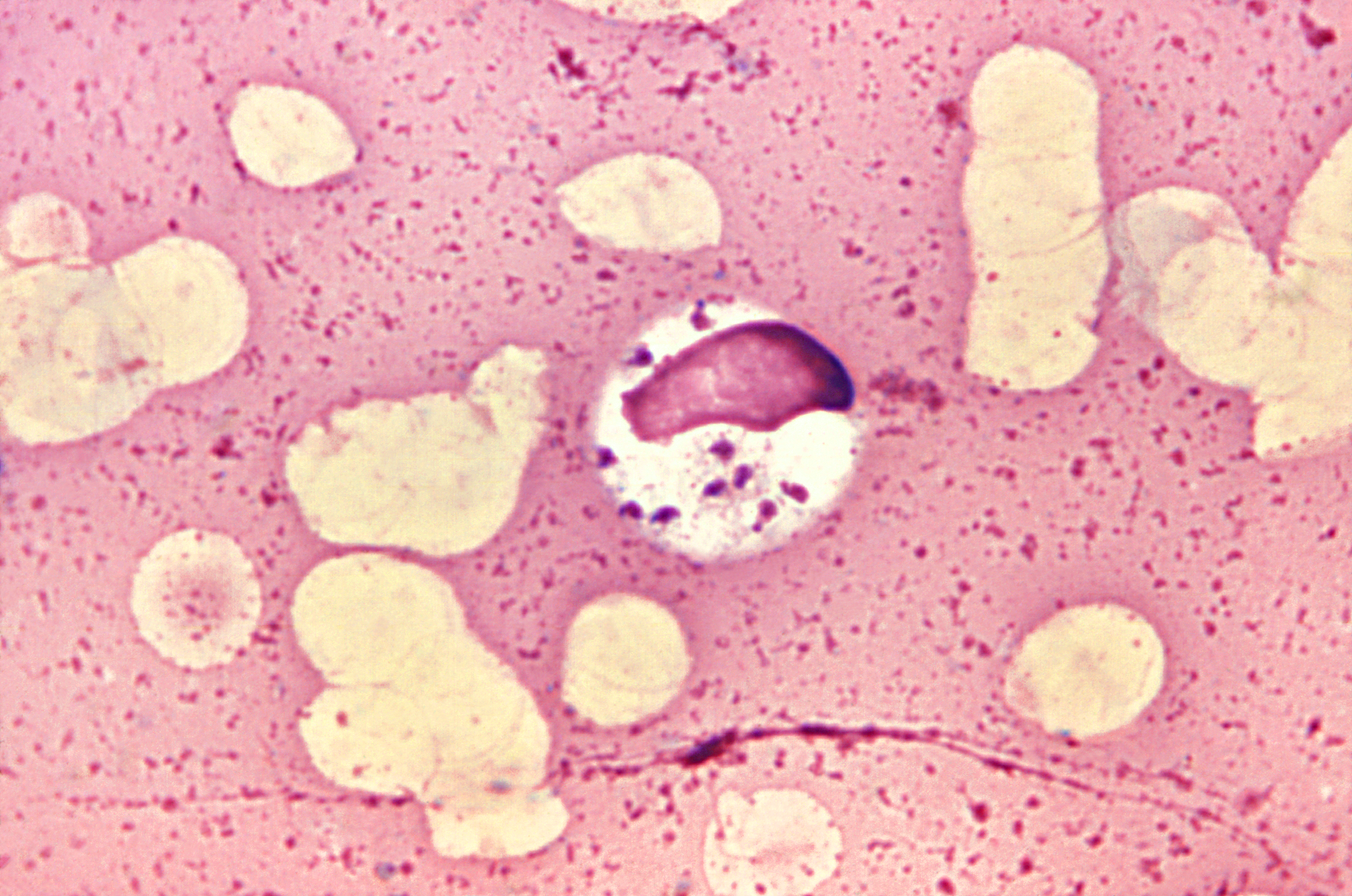 imensions ranging 111 microns to millimetre. and are capable of performing all functions as that of metazoans. They form spores and carry on reproduction by conjugation, onto gamy and cytogamy. Most protozoans are obligate insect pathogens. They do not grow in artificial diet.
imensions ranging 111 microns to millimetre. and are capable of performing all functions as that of metazoans. They form spores and carry on reproduction by conjugation, onto gamy and cytogamy. Most protozoans are obligate insect pathogens. They do not grow in artificial diet.
Insects are parasitized by several classes of protozoa but only Sporozoa and Conidospora cause death of the parasitized hosts. The parasitism is caused by infective food and water within 72 hours of ingestion. Transovarial transmission has also been reported. Braconid parasitoid Cotesiasp. transmits the spores of microsporidia through its contaminated ovipositor from one larva to another. Under moist conditions, spores of microsoporidia remain viable for about 10 to 12 months
but in a dry state at room temperature lose their infective powers within 30 to 35 days. Matessia sp
and Vairimorpha sp. are potential parasites of Helicoverpa armigera and schizogregarine Farinocystes tribolii Weiser has potential for suppression of stored grain pest Tribolium castaneum Herbst.
Diagnosis of protozoan disease on the basis of symptomology is rather difficult affair, as insects dying of this disease show very general symptoms. For identification of protozoan pathogens the diseased host is crushed, body fluid of macerated tissues are stained and the infected stage of protozoa are observed and subjected to histopathological, biochemical and serological tests. Not many protozoa have shown remarkable success in the control of, insect pests. However, two protozoa have shown some degree of success. Characters of these are given below:
Nosema bombysis; This belongs to class micro sporidia. It produces ‘spore singly and possesses sporont diporous with nuclei in diplokaryotic arrangement.
Adelina tribolii: This belongs to sub-class coccidia. This is parasite in fat body and gut wall of insects. Its spore is spherical to sub-oval, macro and microgamete present, cysts with 10 or morte spores, each with two sporonts. Examples of Protozoans causing diseases in insects (included in Microsporidia) are:
- Microsporidium polyhedricum infests tobacco caterpillar
- Perezia pieris parasitizes cabbage butterfly.
- Perezia pyrauste infests the larvae of maize borer.
- Trypanosoma rangeli is pathogenic to reduviid bugs and bed bugs.
Key Reference : Insects and Pests Management by Ali Asghar Hashmi







