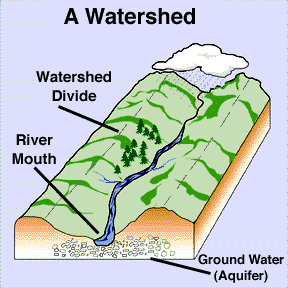
 Definition:
Definition:
“Watershed management is a concept which recognizes the judicious management of three basic resources of soil water and vegetation, on watershed basis, for achieving particular objective for the well being of the people”. It includes treatment of land most suitable biological as well as engineering measures.
Objective of watershed management:
Production of food, fodder, fuel.
Pollution control
Over exploitation of resources should be minimized
Water storage, flood control, checking sedimentation.
Wild life preservation
Erosion control and prevention of soil, degradation and conservation of soil and water.
Employment generation through industrial development dairy fishery production.
Recharging of ground water to provide regular water supply for consumption and industry as well as irrigation.
Recreational facility.
Steps in watershed management:
Watershed management involves determination of alternative land treatment measures for, which information about problems of land, soil, water and vegetation in the watershed is essential.
In order to have a practical solution to above problem it is necessary to go through four phases for a full scale watershed management.
Programme:
Recognition phase.
Restoration phase.
Protection phase.
Improvement phase.
1. Recognition Phase:
It involves following steps
Recognition of the problem
Analysis of the cause of the problem and its effect.
Development of alternative solutions of problem.
Necessary information is obtained from different surveys like soil survey, land capability survey, agronomic survey, forest, engineering and socio economic survey, etc. This information serves as a basis for fixing and determining the watershed problems, priorities in land treatment measures, and causes and effects of problems on land and people.
2. Restoration Phase:
It includes two main steps.
Selection of best solution to problems identified
Application of the solution to the problems of the land
As per the priorities, treatment applied initially to critical areas. After this proper measures like biological and engineering measures are applied to all types of lands.
3. Protection Phase:
This phase takes care of the general health of the watershed and ensures normal functioning. The protection is against all factors which may cause determined in watershed condition.
4. Improvement phase:
This phase deals with overall improvement in the watershed and all land is covered. Attention is paid to agriculture and forest management and production, forage production and pasture management, socio economic conditions to achieve the objectives of watershed management. Health, family planning, improving cattle, poultry, etc. are taken depending upon intensity.







